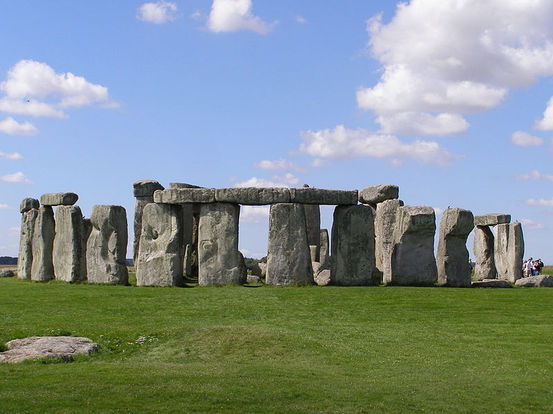
Stonehenge is one of the most famous neolithic (Stone Age) monuments in the world.
The site features the stone circle itself, but also hundreds of other prehistoric monuments scattered around the area.
It’s a "prehistoric" monument, built before the invention of writing.
It originates from the earliest phase of prehistory, the Stone Age, which came before the Bronze Age and Iron Age.
Specifically, it belongs to the later part of the Stone Age, the New Stone Age (Neolithic), following the Old Stone Age (Paleolithic) and Middle Stone Age (Mesolithic).
During the Paleolithic, the first phase of the Stone Age, humans were nomadic hunters who followed large herds of wild animals across the tundra.
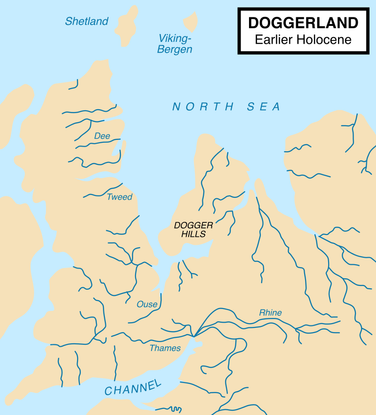
Britain had a harsh climate and was infrequently inhabited.
During the Mesolithic, the second phase of the Stone Age, a warmer climate led to Britain becoming covered in forests.
Humans arrived in Britain and survived on food typically found in wooded areas, including elks, deers, boars…
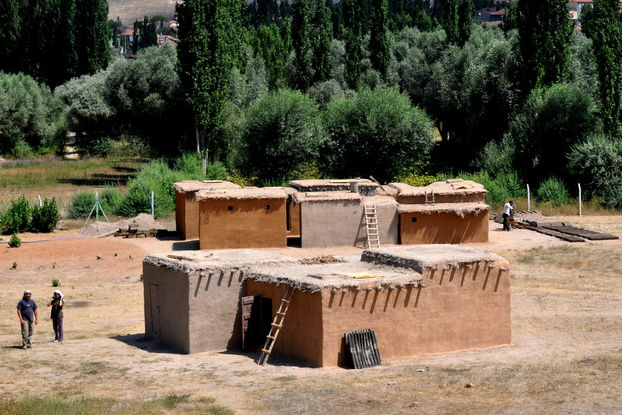
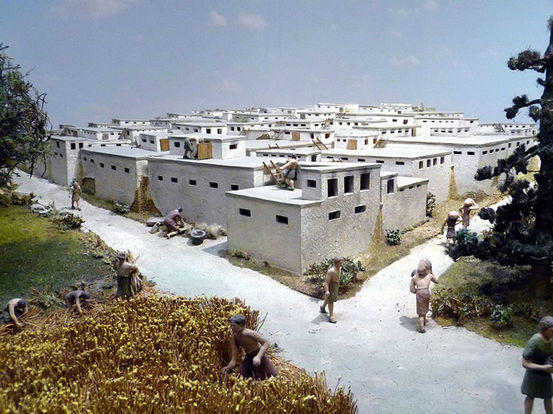
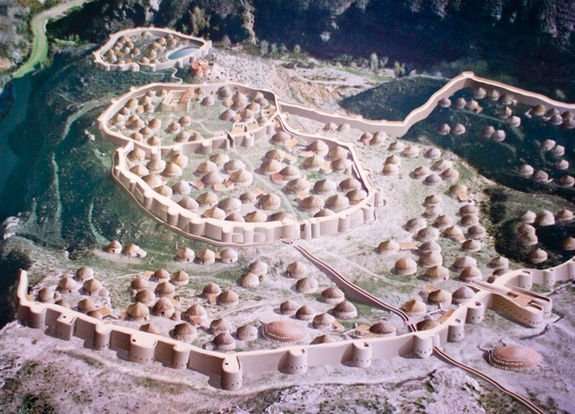
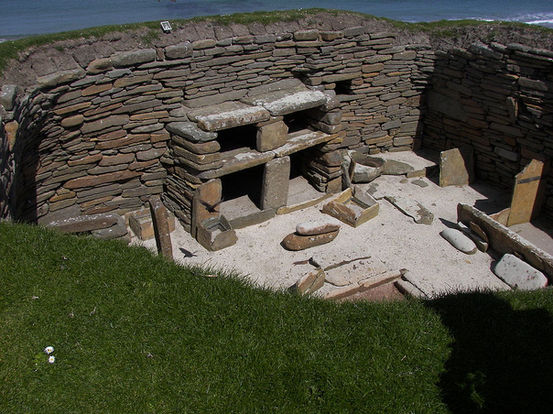
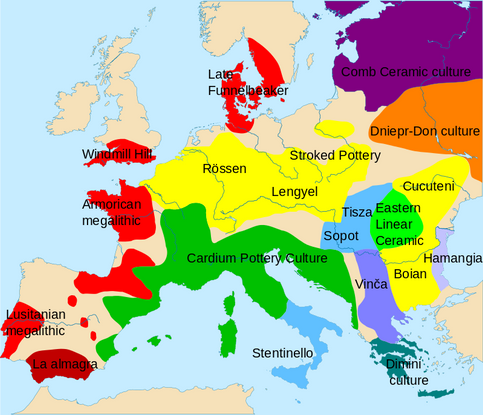
Finally, during the Neolithic, the last phase of the Stone Age, humans transitioned to settling into farming communities.
This shift was enabled by the advent of agriculture in the Middle East, which profoundly changed human lifestyles and their relationship with the environment.
The advantages included the ability to produce food surpluses and build more permanent homes.
However, this also brought significant drawbacks such as increased conflict and the spread of diseases.
It was during this period that humans began constructing massive stone monuments - including Stonehenge.













































.jpeg)